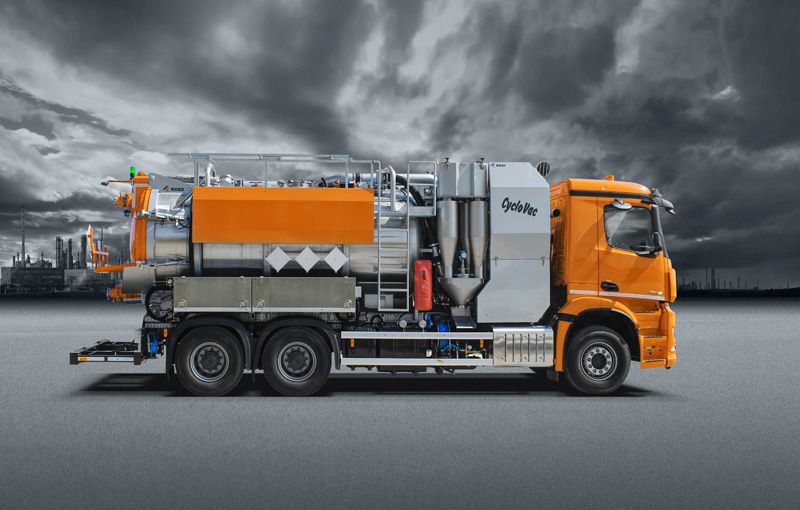
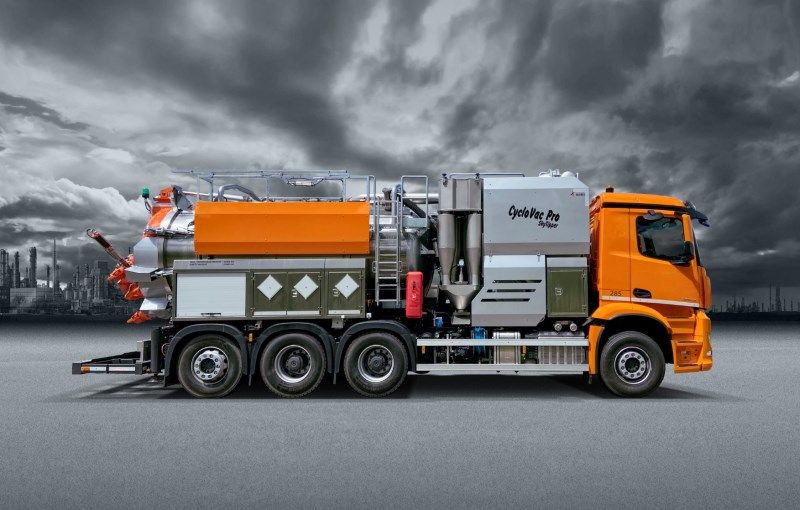
Vacuum truck for working with dry and wet (hazardous) substances in industry
Vacuum trucks - dry - wet

A dry and wet substances vacuum truck (or super sucker) works on the principle of pneumatic transport (air movement). The vacuum tank on the vacuum truck is placed under negative pressure by the large amount of air displacement created by the blower. The air loses its speed in the tank due to the volume increase, as a result, it will no longer be able to carry large quantities of product. In particular, heavier particles will drop down. The air and product is then thrown against the bottom of the vacuum tank, so the speed decreases even more and even more product drops down. This is why dry substances trucks are also called air movement trucks.
In a dry and wet vacuum truck with cyclone separator, the product, which can be both dry and wet, enters the vacuum tank by means of air displacement. The vacuumed product does not end up in the filters and blower; only the vapours (gases) and dust particles go there. There are two types of sensors on the sludge tank (one for dry substances and one for wet substances), which come into operation when the tank is full. In the event of surplus released vapours (gases), a KOKS scrubber can be connected to clean them before they are released into the atmosphere.
Need thorough advice?
We can imagine that you would like to know more about our products, the fields of application and our company. Make an appointment without obligation to get to know us and our extensive range of industrial cleaning machines.
We will be more than willing to tell you why thousands of professionals worldwide trust KOKS Group and KOKS equipment.
You can contact us by calling +31 (0)72 540 66 99, by emailing info@koks.com or by filling in the contact form via the link below. On working days we are available between 07.30 and 17.00 and we are happy to be of service.

Cyclone filter technology
To prevent the dry and wet substances from ending up in the blower, all trucks are fitted with a filter system. This filter system consists of cyclonic filters, which are mounted at the front of the vacuum tank, such as can be seen on the KOKS CycloVac. The final filter/collection container collects the fine dust and must be cleaned regularly.
There are two ways to do this:
- Pneumatic (standard): with an air blast (air return flow) the separated product is blown back into the tank (maintenance-free).
- Mechanical: with pneumatically operated beaters (shaking or vibrating).
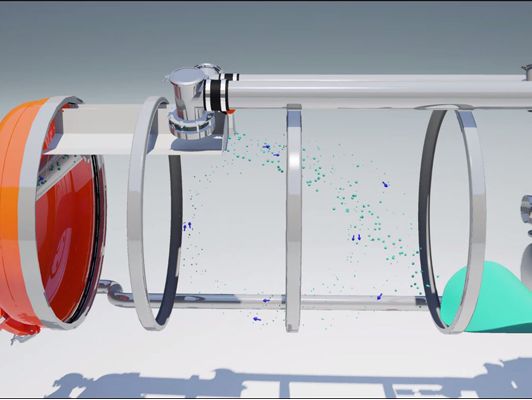
Short description of a dry and wet vacuum truck with cyclone separator
- Volume increase
As the air makes the transition from the suction pipe connection (which is 8'') to the tank (which is bigger than 8''), the heavy parts drop to the bottom of the tank. - Air breaker
Provides an air refraction, which reduces the speed of the lighter particles, which also drop to the bottom. - Cyclone filtration
Finally, the floating parts are removed from the airflow by the swirling and refraction of the air in the cyclone. - End filter
Placed between the blower and the tank to prevent dust penetration.

Safety equipment for dry and wet substances vacuum trucks
Dry and wet substances vacuum trucks with ASME, DOT 407/412 and/or ATEX (Ex) (pump system) approval are equipped with various additional safety equipment, which make them suitable for the transportation of hazardous substances on public roads. These include, for example, impact/roll bars, tank locking, nitrogen connection, etc.

Main components of a dry and wet substances vacuum truck with cyclone separator
- Pressure/vacuum tank (dirt tank and votex pots)
- Pumps and drive (PTOs and blower)
- Filter installation (filter bags and cyclones)
- Various (exchangeable) rear covers (blow, liquid and loose lid)
- Various safety equipment (earthing reel, rupture disk, clamp protection, rear cover protection etc.)
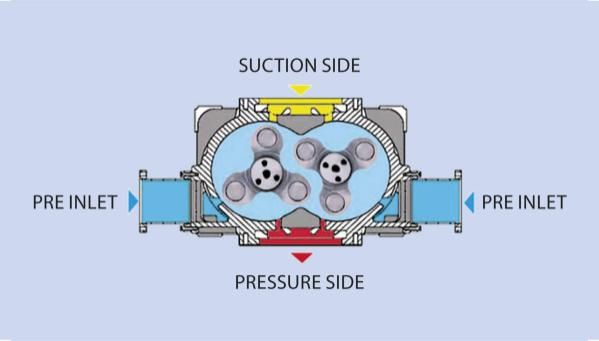
Tri-lobe blower: one of the unique components
The Tri-lobe blower has internal rotors that turn against each other. The type of blower that we use has three lobes per rotor, with as advantage that the three-lobe produces less noise. These lobes roll over each other and do not touch the pump housing. The pump housing is oil-free.
As the rotors turn, air in the inlet is trapped between the rotor lobes and the casing and is carried round to the outlet without being compressed.
The casing bore toward the discharge port is slightly eccentric so that as the lobe approaches the port the gap between it and the casing begins to widen. This allows gradual equalisation of pressure between the air in the discharge port and that in the chamber behind the advancing lobe. Pressure equalisation in two-lobe blocks occurs abruptly as the advancing lobe crosses the lip of the discharge port. This is the main reason why three-lobe blocks generate significantly less pulsation than two-lobe blocks. The air is then finally pushed out against the pressure in the pipework.
If vacuum (yellow) occurs between the rotor and the casing ambient air (blue) enters the blower block via so-called pre-inlet channels as the rotors continue to turn. The two volume flows subsequently combine and the arising compression heat is dissipated throughout a much larger volume of trapped air. This approach therefore achieves the same discharge temperatures that are produced by normal blower blocks.
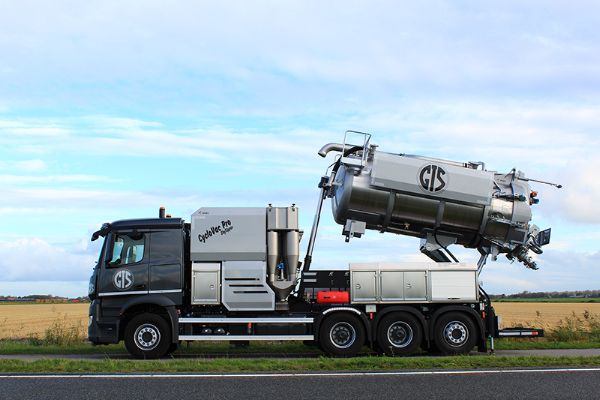

Types of dry and wet substances vacuum trucks and equipment
The operation of a dry and wet substances vacuum truck is based on the movement of substances due to the movement of air, or pneumatic transport. The KOKS MegaVac and the KOKS CycloVac are dry and wet substances trucks that work according to this principle. There is also self-supporting vacuum equipment for dry and wet substances, such as the KOKS MegaVac Loader, KOKS CycloVac Cyclone Loader and KOKS MegaVac Container.

Applications for use of dry and wet substances in vacuum equipment
- Emergency clean-up
- Catalyst work
- Ground suction/excavation work
- Industrial cleaning
- Onshore activities
- Petro-chemical activities
- Well cleaning
- Sewer cleaning
- Shutdown cleaning work
- Silo cleaning
- Transport work
- Vacuum cleaning work
- Water surface cleaning
- Ship cleaning
- Ballast suction
- Suction and blowing of dry and wet substances
- Pressuring liquids
- Oven cleaning
- Fly ash removal
- Blasting grit suction
- Blast furnace slag suction
- Stable/stall cleaning
- Crawl space cleaning





